What is Diagnostic Imaging?
Diagnostic imaging helps doctors pinpoint and treat various medical conditions. With digital x-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds, they can look inside the body to confirm a diagnosis and expedite treatment. State-of-the-art machines take high-quality images so doctors can formulate strategic care plans.
What type of imaging will a doctor order?
The type of imaging a physician orders depends on the patient’s symptoms or condition. It also depends on what part of the body is being examined and how well a patient responds to treatments for illnesses or fractures. Most imaging tests are painless, quick, and easy to perform. Some tests may require patients to lie still for a time inside a machine. While this can be uncomfortable, it is the best way to find out what is going on inside the body.
Diagnostic imaging allows doctors to see parts of the body that is not visible to the naked eye. Advanced medical technology allows for non-invasive ways to see and examine organs, bone, muscle, and blood vessels that were previously only feasible with surgery. Medical facilities with quality diagnostic imaging machines can quickly perform tests that help doctors understand a patient’s medical condition.
What are the types of diagnostic imaging?
Family First ER offers a wide array of emergency diagnostic imaging services. These include:
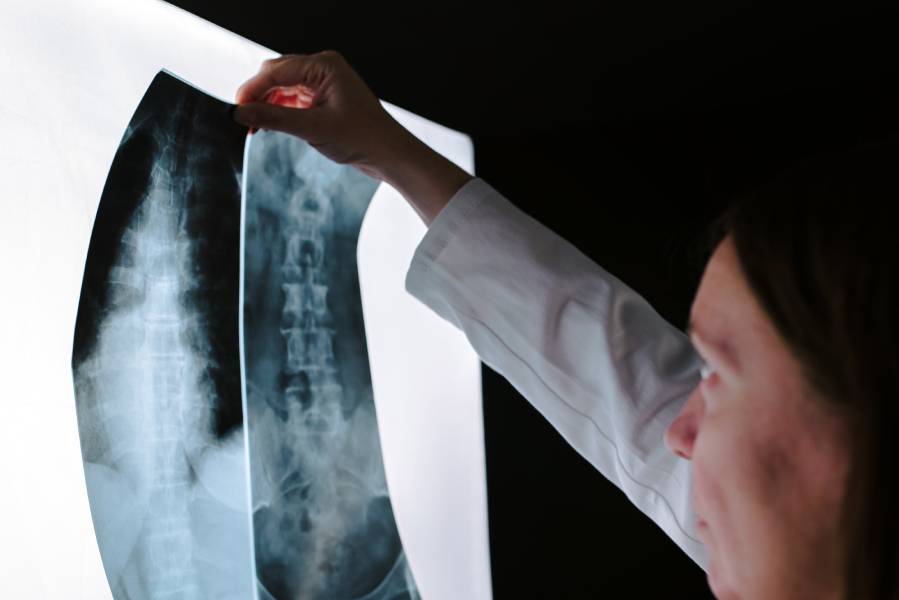
Digital X-Rays
X-rays are commonly used in diagnostic imaging tests. X-ray machines generate high-energy beams pass through organs and soft tissue (but not bone or hard tissue), generating an image of your skeletal structure. X-rays are often use to identify bone injuries.
In recent years, traditional x-rays have received a technological upgrade. In the past, x-ray images usually developed within 15-20 minutes, which caused delays in diagnosing and treating injuries or ailments. Furthermore, the patient would have to wait until the healthcare team viewed the developed images for a diagnosis.
New technologies allow x-rays to be taken digitally. Instead of conventional film, images are captured via electronic sensors and stored on a computer or cloud. These images do not have to develop, meaning they can be viewed immediately to expedite diagnosis and treatments. Digital images can even be enlarged to pinpoint injuries and disease accurately.
CT Scans
Also know as “cat scans,” CT scans combine a string of x-ray scans captured from various angles. CT scans are more detailed than x-rays and are often used to look at larger sections of the body. These scans visualize bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels simultaneously, producing high-quality, cross-sectional images that can be reformatted as three-dimensional or multiple planes.
CT scanners are large tube-like machines that patients usually lay in. Doctors use CT scans to find injuries and diseases that previously could only be found during surgical procedures. CT scans use low levels of radiation and are safe for patients. These non-invasive tests help pinpoint and treat a range of medical illnesses or injuries, including:
- Brain/head injuries, stroke, bleeding, and abnormalities of the skull.
- Congestive chest and respiratory issues; CT scans offer better insight into the lungs and breathing passages than standard x-rays.
- Enlarged glands or lymph nodes in the neck area.
- Spinal problems, herniated discs, fractures, or abscesses.
- Sinus diseases or obstructions in the sinus cavities.
- Pain in the pelvic and abdominal region.
CT scans are even used to find the causes of dizziness and vertigo. Of course, they are also utilized to examine cancer and potentially stop its spread in the body.
Ultrasounds
Ultrasounds are used for an array of diagnostic work. These tests do not use any form of radiation, making it a safe technique to use for pregnant patients. While most people associated ultrasound and sonograms with pregnancy, they are also used to:
- Examine blood vessels around the neck and legs for blockages.
- Visualize internal organs like the gallbladder for stones or soft tissue issues.
- Diagnose thyroid gland problems.
- Diagnose genital abnormalities or irregular growths.
- Look for lumps in the breast that may be cancerous.
Ultrasound can be performed in 2D, 3D, and even 4D. As part of the tests, high-frequency sound waves are emitted from transducers placed against the skin. The sound waves bounce off bones and tissues, producing visible images on a computer for the physician to review.
At Family First ER, we have the latest diagnostic imaging technologies and equipment to visualize bone and soft tissue damages. So whether you need a digital x-ray, CT scan, or ultrasound, we have the tools and expertise to treat all types of injuries or illnesses.

